Navigating the complexities of shipping from China to Amazon FBA in Germany is a operational challenge that directly impacts your cash flow and inventory availability. This definitive guide cuts through the theoretical jargon to deliver a practical, step-by-step playbook. Inside, you'll find precise landed-cost math with worked examples, a clear SOP to avoid customs holds, copy-paste RFQs and contract clauses for brokers, and a actionable vetting matrix—everything you need to compare quotes, ensure compliance, and lower your total cost of ownership for European logistics.
Quick answers
Fastest, small shipments: Express couriers (DHL/UPS/FedEx) or air-express — door-to-door typically 1–5 days.
Cheapest per unit: Sea freight (FCL/LCL) — best for full containers or pallet loads; plan 25–55 days door-to-door for typical China→Germany FCL shipments.
Best balance speed vs cost: China→Europe rail (China-Europe freight) — ~12–20 days to Germany depending on route and final-mile.
Are you ready?
Get real-time quotes for Germany
Get Quotes
Who this is for
Small/medium Amazon FBA sellers needing repeat replenishment from China.
Procurement and operations teams deciding between FCL/LCL/air/rail/express.
Logistics managers who must optimize landed cost and reduce stockouts.
Anyone who needs an actionable step-by-step execution plan for shipping, customs, and last-mile in Germany.
Freight costs from China to Germany
| Transport mode |
Transport type |
Example cost (market example) |
Typical transit time (market example) |
Applicability |
| Sea freight |
20' container (FCL) |
$1,400 → Hamburg |
20–30 days |
Bulk, cost-sensitive shipments |
| |
40' container (FCL) |
$2,350 → Hamburg |
20–30 days |
Large volume or consolidated loads |
| |
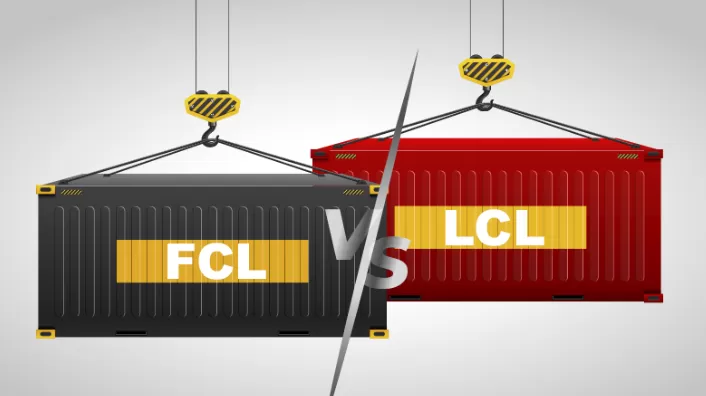
LCL |
$270 – $580 per CBM (benchmark range; route/service-dependent) |
20–32 days |
Small shipments, flexible capacity. Example public benchmarks: $269.65–$298.03/CBM and $578/CBM depending on provider/service. |
| Rail freight |
20' container |
$5,000 → Hamburg / $5,300 → Munich |
14–18 days |
Faster than sea, reliable to inland hubs |
| |
40' container |
$7,100 → Hamburg / $7,450 → Munich |
14–18 days |
Predictable delivery for larger shipments |
| Air freight |
Air cargo (consolidated) |
$4.00 / kg (>1000 kg) |
4–7 days |
High-value, urgent, time-sensitive goods |
Core prerequisites before you book anything
Decide Incoterm (EXW / FOB / CIF / DDP). Incoterms determine who pays/export vs import responsibilities.
Obtain/importer IDs: EORI is mandatory for EU customs declarations — get one before first import.
HS codes & landed cost plan: classify goods (HS code) and estimate duties + VAT to build landed cost.
Packaging & labelling: especially for Amazon FBA — FNSKU, carton labels, and pallet rules. See FBA section.
Major origin ports in China & German arrival ports (what to pick and why)
Main China origin hubs
Shanghai / Ningbo / Qingdao — strongest FCL network, many carriers, competitive rates.
Shenzhen (Yantian / Shekou) — south China, good for Shenzhen/Guangzhou factories and fast sailings to northern Europe via feeder.
Xiamen / Guangzhou — regional options; LCL and feeder services common.
Major Germany destination ports / gateways
Hamburg — primary container port for northern Germany; deepwater, multiple carriers, good hinterland connections.
Bremerhaven — very high container throughput; commonly used for transshipment and large inbound flows.
Wilhelmshaven — growing, sometimes used for direct deepwater services and to relieve congestion.
Rotterdam (Netherlands) / Antwerp (Belgium) — often used as economical European gateways with efficient hinterland trucking to Germany. Choose if you want lower ocean costs and reliable inland trucking.
How to pick: If your consignee is northern Germany (Hamburg/Bremen area) choose Hamburg/Bremerhaven. If inland (Bavaria, Baden-Württemberg) compare door-delivery drayage from Rotterdam vs Hamburg — sometimes Rotterdam + road is cheaper.
freight forwarding
Get real-time quotes for Germany
Get Quotes
Shipping From China To Germany Sea freight (FCL & LCL)
When to use
Large restocks (full container), predictable cycles, or when unit cost is priority.
End-to-end steps (port-to-port and door-to-door differences included)
Order & prep at supplier (0–7 days)
Confirm production finish date, pack specs, and palletization. Confirm Incoterm and who provides export docs.
Pre-carriage (factory → origin port) (1–3 days typical)
Local trucking, export packing, and stuffing (if FCL). For LCL, shipper delivers to consolidation warehouse for stuffing by consolidator.
Export customs & port cut-off (1–3 days)
Submit export declaration. Factor in extra time if goods require inspection or export license.
Ocean main leg (port-to-port) — 20–40 days typical China→Germany ocean transit; some lanes extend beyond 40 days depending on route and transshipment.
Port operations & import customs (1–5 days)
Container discharge, customs release, duties & VAT calculation. Ensure importer has EORI and VAT arrangements.
Inland delivery / drayage to warehouse (1–5 days)
Pay detention/demurrage attention: return container within free days to avoid fees.
Time estimate summary (door-to-door)
FCL: 25–55 days door-to-door depending on origin port, transshipment, and local delivery.
LCL: Add consolidation time and possible delays; plan +7–14 days vs FCL.
Cost drivers & optimization
Drivers: bunker/seasonal surcharges, container availability, port congestion, distance to inland delivery.
Save: book early for peak seasons, use direct services where possible, consider 40’HC for better unit economics, and renegotiate long-term rates with carriers.
Sea-Express / “Sea-Fast”— practical use & steps
What it is
A hybrid: prioritized sea services, dedicated weekly slots or feeder/express container services with fewer stops. Faster than standard LCL/FCL and cheaper than air.
Steps & timeline
Procedures mirror sea freight — but expect ~18–30 days ocean time on specialist routes (some direct services reach ~22-26 days). Use when inventory risk requires faster replacement but you can’t afford air.
Pro tips
Check if your freight forwarder offers a guaranteed transit time product; verify cancellation/compensation terms if the promised windows are missed.
Sea + Truck (Sea-Card) — multi-modal for inland reach
Use case
Ship to a major European hub (Rotterdam/Antwerp) then truck to Germany warehouses. Cost-effective for inland deliveries beyond port hinterland.
Steps
Ocean leg to Rotterdam/Antwerp (20–35 days)
Quick truck transfer to German hub — typically 1–3 days for northern Germany, 2–5 days deeper inland.
Customs clearance either at port or at inland customs office, depending on arrangements.
When to pick
When you get better ocean rate to Netherlands/Belgium hubs and trucking to Germany is cheaper than direct ocean to German ports.
Air freight (airport-to-airport and door-to-door)
When to use
Urgent replenishment, high-value inventory, or time-sensitive orders (seasonal fashion, shortage recovery).
Typical steps (door-to-door)
Book flight / AWB (0–1 day)
Export customs & security checks (1 day typical; +1–3 days if inspected)
Air transport (1–3 days depending on routing)
Import customs & delivery (1–3 days)
Door-to-door total: 3–10 days typically.
Pricing & geometry risk
Air billing uses chargeable weight (actual vs dimensional). For bulky light goods, air is often prohibitively expensive.
Operational tips
Use consolidated air (air cargo consolidators) for smaller shipments to reduce cost. Pre-book space during peak seasons.
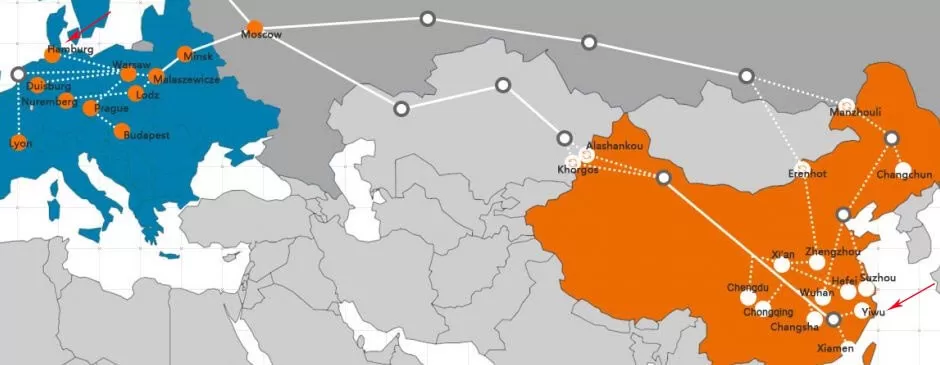
Shipping From China To Germany Rail (China → Europe — China-Europe freight)
Why consider it
Faster than sea, cheaper than air — sweet spot for medium-value goods that need speed but not urgent same-week transit.
Typical timeline and routes
12–20 days China to Europe; to Germany specifically expect ~15 days to terminal plus last-mile 2–5 days depending on final destination. Actual times depend on corridor (via Poland, Belarus, or Russia) and border handling.
Steps
Inland trucking to rail terminal (1–3 days)
Rail transit (12–20 days)
Border handling & gauge changes (if crossing differing track gauges)
Transshipment at EU terminal and customs (2–5 days)
Final-mile truck to warehouse (1–4 days)
Risks & checks
Some routes may face geopolitical disruptions; pick operators with stable European intermodal partnerships.
Door-to-door vs Port-to-port — what middle ground makes sense
Door-to-door: best for small/medium importers who lack local customs capacity — one contract covers everything. Slightly higher cost, much less operational risk.
Port-to-port: for cost-sensitive importers with customs clearance and inland logistics capabilities; cheaper but higher operational burden.
Amazon FBA (SMB buyer) — end-to-end for shipments to EU FBA (Germany)
Core constraints & rules
Follow Amazon’s packing, labelling, and carton requirements exactly. Non-compliance can lead to refused inbound or chargebacks. Use Amazon’s inbound guides.
For EU imports, you must handle EORI and VAT arrangements before arrival. Amazon and third-party providers (Amazon Global Logistics included) offer integrated FBA shipping services.
Typical FBA path (practical checklist)
Create shipment in Seller Central — choose destination country and FBA warehouse.
Label and pack at origin — FNSKU on every unit, cartons labeled with Amazon carton labels, and palletize per Amazon spec (1–3 days).
Pick mode:
Samples / small restock: Express or air (fast, costly).
Routine replenishment (pallets): LCL or rail for cost-savings.
Large restock: FCL ocean.
Book carrier and inform freight forwarder of FBA requirements — forwarder must deliver to the specific Amazon receiving address and adhere to appointment windows.
Customs & import — ensure VAT/EORI and import paperwork are in order; for DDP, shipper covers import formalities.
Pre-advise Amazon & confirm appointment — some FBA centers require appointments and specific delivery windows; coordinate with your forwarder.
Amazon receives & processes — time in-warehouse varies; allow 3–10 days for processing depending on workload.
Decision points for sellers
If you’re nervous about customs or inbound compliance, use DDP or Amazon Global Logistics to remove friction. Amazon’s services can be more expensive but reduce listing downtime.
Customs Clearance — A Practical SOP for Shipping from China to Germany
A compact, action-oriented customs checklist that operations teams can follow end-to-end. Each step states who normally does it, what documents are required, typical time, common hold-ups and the practical fix.
Quick summary (one-line)
Import clearance is the electronic declaration of goods’ description, value and origin to German/EU customs (ATLAS/TARIC). The Importer of Record (IOR) or its appointed customs broker submits the declaration and pays duties/VAT before goods are released.
High-level workflow (9 steps & timing)
Prep documents & classify HS code — Seller/Buyer: 0.5–5 days.
Shipment & in-transit — Carrier/Forwarder: variable by mode.
Pre-arrival notification (manifest) — Forwarder: 0–2 days before arrival.
Import declaration (electronic) — Customs broker: same day–1 day.
Customs risk assessment & possible physical inspection — Customs: instant–several days if inspected.
Pay duties & VAT (or lodge a guarantee) — Importer/broker: same day–short term.
Customs release — Customs: after payment/inspection.
Pickup / final delivery — Carrier/forwarder: 1–5 days.
Post-import compliance (Intrastat/VAT returns) — Importer/accounting: ongoing.
Roles & who does what
Seller: confirms Incoterm, provides Commercial Invoice, Packing List, Certificate of Origin and any certificates (CE, test reports, licences).
Buyer / Importer of Record (IOR): holds EORI number, ensures VAT arrangements and pays import taxes (unless contract states otherwise).
Freight forwarder: handles transport, pre-arrival manifest, chooses consolidation options, and coordinates delivery.
Customs broker / agent: files the electronic declaration (ATLAS/SAD), responds to customs queries, pays duties or arranges guarantees.
Required documents (always check consistency)
Commercial Invoice — accurate description, HS code, unit price, totals, Incoterm.
Packing List — box counts, dimensions, gross/net weights.
Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB).
Certificate of Origin (if preferential tariff or required).
Any product-specific certificates (CE, RoHS, medical approvals, battery documentation, etc.).
Importer’s EORI number.
freight forwarding
Get real-time quotes for Germany
Get Quotes
Step-by-step operational SOP (detailed)
Before shipment
Confirm Incoterm in contract (EXW/FOB/CIF/DDP). Incoterm decides who is responsible for import clearance.
Validate HS codes via TARIC and estimate duties & VAT.
Collect Commercial Invoice, Packing List, COO and test reports (if required).
While in transit
Forwarder uploads manifest and ETA to customs. Consider pre-lodgement to speed release.
For LCL, ensure master & house B/L details match the packing list and HBL.
At arrival
Customs broker files the electronic import declaration (ATLAS/SAD). Include exact invoice values and HS code.
Customs runs automated risk checks—be ready to supply extra docs.
If selected for physical inspection, arrange immediate access and provide photos/test reports.
Payment & release
Pay assessed customs duty and VAT, or provide an approved guarantee. After payment and any inspection, customs issues release and goods can be collected.
After release
Complete Intrastat (if thresholds met) and record VAT input for reclaim where eligible. Keep all documents for audits.
Common hold-ups and fixes
No or incorrect EORI → delay: Fix—apply for EORI before first import.
HS code mismatch / vague descriptions → risk of inspection: Fix—use TARIC for exact codes and keep technical specs on hand.
Invoice discrepancies (value/quantities) → customs audit: Fix—align invoice, contract and payment proof.
Missing conformity certificates (CE, battery test reports, licences) → detention: Fix—obtain certificates before shipment or arrange inspection/testing immediately.
Demurrage/detention at port → escalating costs: Fix—ensure timely customs clearance and pre-book drayage/pickup.
Modal differences (practical notes)
FCL: declaration is straightforward; main delays are inspection or port congestion. Ensure VGM and stuffing photos.
LCL: higher chance of mismatched HBL/HBL errors—consolidator must supply correct house/master docs.
Air & Express: fast clearance but ensure AWB, invoice and EORI are correct; courier often handles small shipments and VAT on behalf of consignee.
Rail: similar to sea for customs at EU terminal—allow time for transshipment handling and inland delivery.
Quick landed-cost formula (use this to budget)
Example inputs: FOB $10,000; freight $1,200; insurance $50; duty rate 3%; VAT 19%.
CIF = FOB + freight + insurance = 10,000 + 1,200 + 50 = 11,250.00
Customs duty = CIF × 3% = 11,250.00 × 0.03 = 337.50
VAT base = CIF + duty = 11,250.00 + 337.50 = 11,587.50
VAT = VAT base × 19% = 11,587.50 × 0.19 = 2,201.63
Total import taxes = duty + VAT = 337.50 + 2,201.63 = 2,539.13
Use this template to produce a live landed-cost estimate before ordering.
Amazon FBA
Get real-time quotes for Germany
Get Quotes
Amazon FBA — must-do items for sellers
Follow Amazon’s carton, pallet and labelling specs exactly. Non-compliance can cause inbound refusals and rework charges.
Confirm whether to ship DDP (shipper pays duties & VAT) or DAP (buyer handles customs). For SMBs, DDP or a forwarder offering “FBA-ready” DDP service reduces risks.
Pre-notify Amazon and book delivery appointments through your forwarder.
Emergency flow — if goods are detained
Contact the broker/forwarder immediately and request the exact customs reason.
Provide missing documents (test certificates, invoices, contracts) within the timeframe.
If value is disputed, submit contracts, payment receipts and packing evidence.
If unresolved, consider re-export or customs sanctioned disposal (costly—use as last resort).
Pre-shipment checklist (copy to SOP)
Incoterm confirmed and recorded.
EORI number ready.
HS code checked in TARIC.
Commercial Invoice & Packing List verified and consistent.
Required certificates available (COO, CE, battery docs, licences).
Freight and insurance numbers set; forwarder chosen with German customs experience.
For FBA: Amazon labels and appointment plan confirmed.
Sample cost and transit examples
Shanghai → Hamburg (FCL 40’HC): typical market range observed recently — example $4,900–$6,500 and 40–69 days door-to-door on some routes (example quotes vary by currency & season). Use live quoting platforms for exact numbers.
Air freight (paletized): market varies by kg and volume; check with consolidators and compare dimensional weight calculations.
Always label these sample numbers as “market examples” and replace with live quotes before publishing or booking.
Risk management, insurance & claims
Insure high-value shipments (All-Risk recommended); cost ~0.3–0.5% of invoice value typically, depending on route and commodity.
Document everything: photos at stuffing, weight surveys, B/L/AWB, commercial invoice.
Claims timeline: notify carrier and insurer immediately on damage/loss; preserve packaging and document damage with timestamps.
Tactical playbooks — choose one and use it
Playbook A — Amazon FBA SMB (cost-sensitive, predictable cadence)
Use FCL when monthly demand > 5–10 pallets; LCL or rail for <5 pallets but >1 pallet. Consider air for emergency replenishment. Use DDP or an experienced EU customs broker to avoid import holds.
Playbook B — Fast replenishment (no stockouts)
Keep a small buffer via air or express, recurring rail shipments for steady restock to cut cost but maintain speed.
Playbook C — Lowest landed cost (less urgency)
Plan 60–90 days ahead, use FCL ocean, ship out of Shanghai/Ningbo, accept longer lead time for lower per-unit cost.
Shipping From China To Germany ddp shipping
1. DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) Core Definition
Liability Allocation:
Chinese supplier assumes full responsibility for:
Export customs clearance
International freight
German import clearance
Payment of all duties/taxes (customs duties, 19% VAT)
Final delivery to designated German address
Risk transfers to buyer upon signed delivery receipt
Applicable Scenarios:
German buyers requiring "all-inclusive door delivery"
High-value or regulated goods (e.g., medical devices, electronics)
B2B e-commerce shipments (particularly Amazon FBA shipments)
2. DDP Operational Workflow
Phase 1: China Export Preparation
Product Compliance Verification:
Mandatory certifications: CE (electronics/machinery), LFGB (food contact materials), GS (safety equipment)
Chemical substances: REACH/CLP registration (PFAS restrictions enforced per EU Regulation 2023/707)
Export Documentation:
Commercial invoice (must state "DDP Incoterms® 2020")
Packing list with HS codes
Certificate of Origin (Form A for GSP tariff preference)
Bill of Lading/Air Waybill
Phase 3: German Customs Clearance Protocol
Tax Registration Requirements:
Non-EU entities must appoint German fiscal representative (IOSS registration mandatory since Jan 2025)
Import VAT calculation: (CIF value + customs duty + clearance fees) × 19%
Clearance Documentation:
EUR.1 Certificate of Origin
ATLAS import declaration
Entry Summary Declaration (ENS)
Compliance Audits:
Electrical/electronic goods: Valid WEEE-Reg.-Nr.
Packaging: VerpackG registration number
Textiles: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 certification
Phase 4: Germany Final Delivery
Last-Mile Carriers: DHL Freight, DB Schenker, DPD (palletized), GLS (parcels)
Delivery Specifications:
Pallets must comply with EPAL EUR standards
ADR documents required for hazardous materials
Amazon FBA shipments: Appointment scheduling via Vendor Central
3. DDP Cost Structure
Total Cost Components:
| Category |
Cost Elements |
2025 Cost Drivers |
| China Local Costs (30%) |
Export declaration, Commodity inspection, Packaging labeling |
Labor cost increase (8.2% YoY) |
| German Duties/Taxes (20%) |
Customs duty (HS-code specific), Import VAT, Customs bond fee |
VAT ID verification fee (€45/entry) |
| Destination Charges (10%) |
Port handling, Delivery order fee, Carrier fuel surcharge |
German minimum wage €14.2/hour |
Critical Cost Controls:
Customs inspection fees: €350-600 per examination (Hamburg port)
Demurrage charges: €120/day after 48-hour free period
Tax optimization: Utilize postponed VAT accounting (PVA) via § 21c UStG
4. DDP Provider Selection Criteria
German Customs Expertise: In-house clearance team with Hauptzollamt accreditation
Valid Credentials: DE EORI number + St.-Nr. tax identification
Compliance Infrastructure: Real-time tracking with API integration capability
Risk Mitigation: All-risk insurance coverage (min. 110% CIF value)
Contingency Resources: EU warehousing network for storage/re-export
5. Risk Management Protocol
| Risk |
Mitigation Strategy |
| Customs Delays |
Pre-clearance HS code binding via Binding Tariff Information (BTI) |
| Tax Liability Disputes |
Contract clause: "DDP costs capped at [X]% of invoice value" |
| Buyer Non-Payment |
30% advance payment + retention of title until full payment |
| Regulatory Changes |
Monthly compliance bulletin monitoring EU Delegated Regulations |
6. 2025 Regulatory Impact Analysis
Carbon Border Adjustment (CBAM): Phase 3 implementation - steel/aluminum imports require verified emissions reports
Supply Chain Act (LkSG): Documentation of ESG due diligence for batteries/electronics (per EU Battery Regulation 2025/1296)
Digital Clearance Platform (DCP): Mandatory electronic filing for all import declarations (Zollformular 0300)
7. Operational Recommendations
For high-volume shippers: Apply for Authorized Economic Operator (AEO) status to reduce physical inspections
VAT optimization: File monthly VAT returns via § 18 UStG to accelerate cash flow
Document retention: Maintain commercial records for 10 years per § 147 AO
Compliance Note: As of Q3 2025, all Chinese exporters must register with German Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes for packaging/electronics prior to shipment.
This framework reflects current Germany-China trade regulations as of September 2025. Validate HS codes via German Binding Tariff Information (BTI) system before shipment execution.
Amazon FBA
Get real-time quotes for Germany
Get Quotes
Shipping From China To Germany DHL Shipping
Core DHL Services
DHL Express
Delivery: 3-5 days (door-to-door)
Use Cases: Urgent shipments ≤70kg (e.g., samples, spare parts)
2025 Rate: ¥420/0.5kg (Shenzhen→Berlin) Includes 18.5% fuel surcharge
DHL Heavy Goods
Delivery: 6-8 days
Use Cases: Pallets/crates (70-300kg; machinery, equipment)
Key Benefit: No delivery appointment fees in Germany
DHL eCommerce
Delivery: 12-15 days
Use Cases: B2C parcels (from ¥85/0.5kg)
Feature: IOSS VAT collection & automated customs filing
Cost Example
Shenzhen→Hamburg | 80kg Bluetooth Headsets | Declared €1,200
China ops: ¥360
Freight: ¥2,150 (Heavy Goods)
German VAT: €228 (19%)
Clearance: €85
Total: ~¥4,200 (€538)
Tip: Use DHL’s VAT deferment to delay tax payment 90 days.
Critical Compliance Notes
Labeling: Electronics require 2x2cm WEEE symbol (€2,000 fine if missing)
Packaging: No straw/raw wood; >30kg boxes need "Team Lift" tags
Timing: Avoid Sunday deliveries; add +3 days during Christmas peak
Pro Tips
Small Shipments: DHL Express + Pre-Clearance (€35; 2hr release)
Heavy Cargo: Negotiate monthly billing (saves 12%)
eCommerce: Always provide IOSS to prevent clearance delays
Use DHL MyGTS for real-time tracking and automated documentation. For high-value goods, activate Tax Shield to transfer duty dispute risks to DHL.
FAQ
Q1 — How long is sea freight from China to Germany?
Typical port-to-port ocean transit is 20–40 days depending on route; door-to-door for FCL often 25–55 days factoring pre/post-carriage and customs. Use live quotes for current windows.
Q2 — Do I need an EORI number?
Yes — any importer into the EU must have an EORI number to lodge customs declarations. Apply before first import.
Q3 — What’s better for Amazon FBA — sea or air?
If cost sensitivity is primary and you can plan, sea (FCL/LCL); if speed and avoiding stockouts matter, use air/express for emergency replenishment. Amazon Global Logistics offers integrated options to reduce friction.
Q4 — How long is rail freight to Germany?
Rail usually reaches Europe in ~12–20 days, with final delivery in Germany typically within ~15–20 days depending on the terminal and last-mile.
Q5 — How do I avoid demurrage?
Return empty containers within free days, pre-pay or arrange quick clearance, have duty/VAT funds available, and pre-book inland transport.
Q6 — Can my freight forwarder act as the Importer of Record (IOR)?
6Yes, many forwarders offer IOR services, but it’s a legal appointment. The forwarder will declare on your behalf, handle VAT/duties and accept legal responsibility for the import. Use IOR only with a reputable provider, confirm who holds liability for fines, and get the arrangement in writing (service contract + power of attorney).
Q7 — What insurance should I buy and when do I file a claim?
Buy cargo insurance (All-Risk or Named Perils) before the goods leave origin. All-Risk covers most loss/damage; Named Perils covers specified events. If damage/loss occurs, document everything (photos, weights, packing, B/L/AWB), notify carrier and insurer immediately, and file a claim within the insurer’s stated deadline. Don’t throw away packaging or evidence.
Q8 — Are lithium batteries and similar regulated items allowed — and what extra steps are needed?
AThey’re allowed but tightly regulated. Lithium batteries require special packing, labeling, documentation and often airline/shipper approval. For Germany/EU you may also need conformity testing and battery declarations. Always declare DG (dangerous goods) early and use a forwarder experienced in batteries.
Q9 — What is a Binding Tariff Information (BTI) and when should I apply for one?
A BTI is an official ruling that fixes the HS code for a product for up to three years. Apply when you import a product that’s hard to classify or if small tariff differences materially affect landed cost. A BTI removes classification uncertainty and reduces risk of retrospective customs re-assessments.
Q10 — Can I consolidate shipments from multiple suppliers into one FCL to save cost?
Yes — consolidation (multi-supplier FCL) is common and cost-effective, but it adds complexity: you must coordinate packing lists, lead times, and who supplies the master/house B/L. Use a consolidator or freight forwarder to manage stuffing, document consistency and customs declarations; plan extra buffer time for supplier coordination.
Explore Our Global Logistics Network
While this guide has equipped you with the knowledge to master shipping from China to Germany, your global supply chain might extend further. We have created comprehensive resources for other major logistics corridors and markets:
United States: Comprehensive US shipping guide with FBA specifics
Canada: Ultimate guide to using a Canada FBA freight forwarder
European Markets: Best freight forwarders for European FBA
Key US Hubs: Detailed insights for New York, Los Angeles, and Chicago
Logistics Fundamentals: Understanding the Differences Between 1PL, 2PL, 3PL, and 4PL
Compare All Options
Each destination and logistics model offers unique advantages depending on your cargo type, volume, and final distribution strategy. Explore our detailed guides for Miami and other major global hubs to develop a truly optimal and cost-effective supply chain.

 EN
EN
 FR
FR
 ES
ES
 JA
JA
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 AR
AR